National Service Hotline
Products
GHS-A
Product model:
- Product Features
- Technical Parameters
- Dimensions
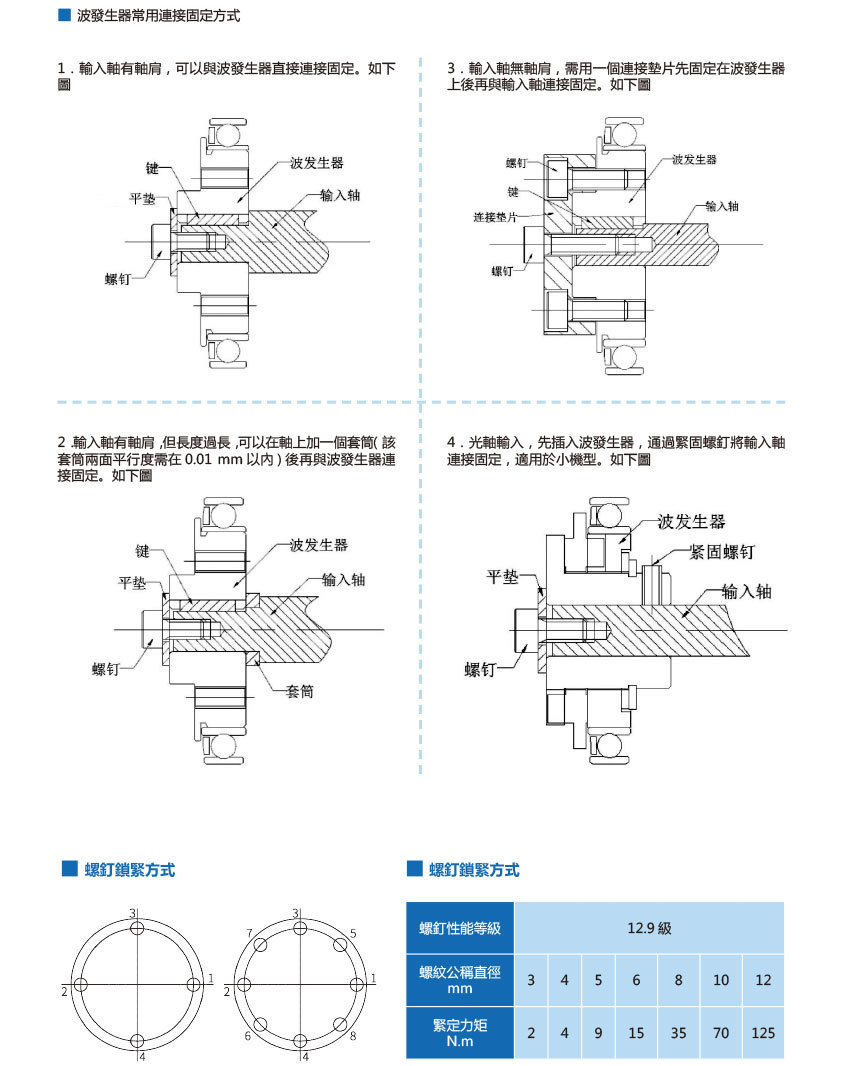
- Installation Instructions
- Download
-
- Commodity name: GHS-A
A Series Self-aligning Type: The flexible wheel features a hollow flanged standard structure, with a compact overall design. The input shaft is connected to the inner hole of the wave generator via a cross slider coupling. Features: ● Flat shape • Standard structure ● Compact and simple design ● No tooth gap ● Automatic self-alignment of the wave generator
Characteristics of Harmonic Reducers:
■ High Precision:
Using advanced design technology and ANSYS software simulation technology, design errors are accurately controlled to below 1 micron. The flexible bearings, cross bearings, flexible wheels, and rigid wheels are processed using precision advanced equipment commonly used in the industry.
■ Large Transmission Ratio:
This design complies with relevant international standards, with a single-stage harmonic gear transmission ratio reaching i=50 to 160. The simple structure of the three basic components on the same axis allows for a high reduction ratio.
■ High Load Capacity:
The flexible wheel and rigid wheel use an arc-shaped gear profile, with tooth-to-tooth engagement being surface contact. At the same time, the number of engaged teeth is relatively large, resulting in a smaller unit area load and a higher load capacity compared to other transmission forms. The use of cross bearings internally effectively increases the load capacity.
■ Compact and Lightweight:
Using integrated design and high-performance materials, the size and weight are significantly reduced compared to ordinary gear devices.
■ Smooth Transmission:
Using advanced 3D simulation design technology and high-precision processing technology, the accuracy of key components is improved, resulting in minimal deformation and smooth transmission. High-performance lubricants are used to reduce impact and noise.
■ Long Lifespan:
Using high-strength, high-performance materials and advanced surface heat treatment processes and coating technologies, the wear resistance of key component surfaces is increased by more than three times, greatly extending the product's lifespan.
■ Principle of Harmonic Gear Transmission
Harmonic gear transmission was invented by American inventor C.W. Musser in 1955. It is a new type of transmission method that utilizes the elastic deformation of flexible working components for motion or power transmission, overturning the traditional mechanical transmission model that uses rigid components, thus achieving a series of special functions that are difficult to attain with other transmissions. The deformation process of the intermediate flexible component is essentially a symmetrical harmonic, hence the name.
■ Composition of Harmonic Gear Transmission Devices
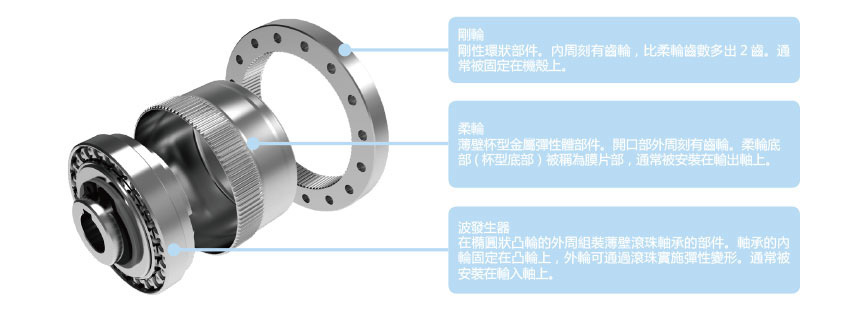
■ Principle of Harmonic Gear Transmission Reduction
The principle of harmonic gear transmission reduction utilizes the relative motion of the flexible wheel, rigid wheel, and wave generator, mainly relying on the controllable elastic deformation of the flexible wheel to achieve motion and power transmission. The elliptical cam inside the wave generator rotates within the flexible wheel, causing deformation of the flexible wheel. When the teeth of the flexible wheel at the ends of the long axis of the elliptical cam engage with the teeth of the rigid wheel, the teeth of the flexible wheel at the ends of the short axis disengage from the teeth of the rigid wheel. The teeth between the long and short axes of the wave generator gradually enter a semi-engaged state along different segments of the circumference of the flexible and rigid wheels, referred to as engagement. The gradual exit from the semi-engaged state is referred to as disengagement. As the wave generator continuously rotates, the flexible wheel undergoes continuous deformation, causing the teeth of the two wheels to constantly change their original working states in four types of motion: engagement, semi-engagement, disengagement, and disengagement, achieving motion transfer from the active wave generator to the flexible wheel.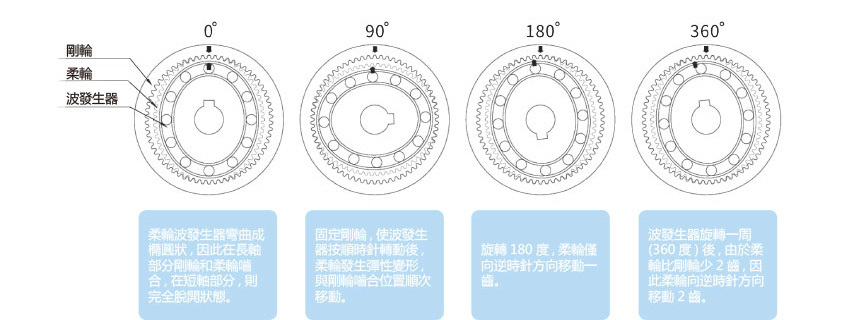
-
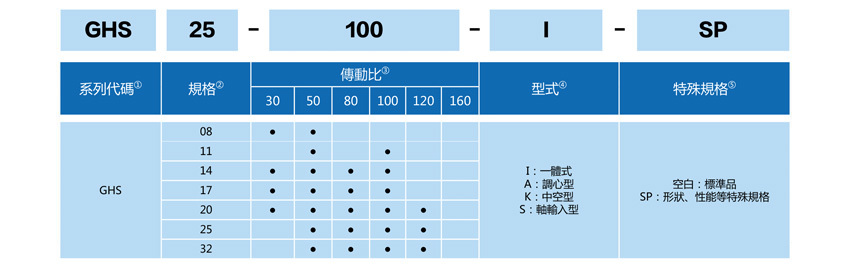
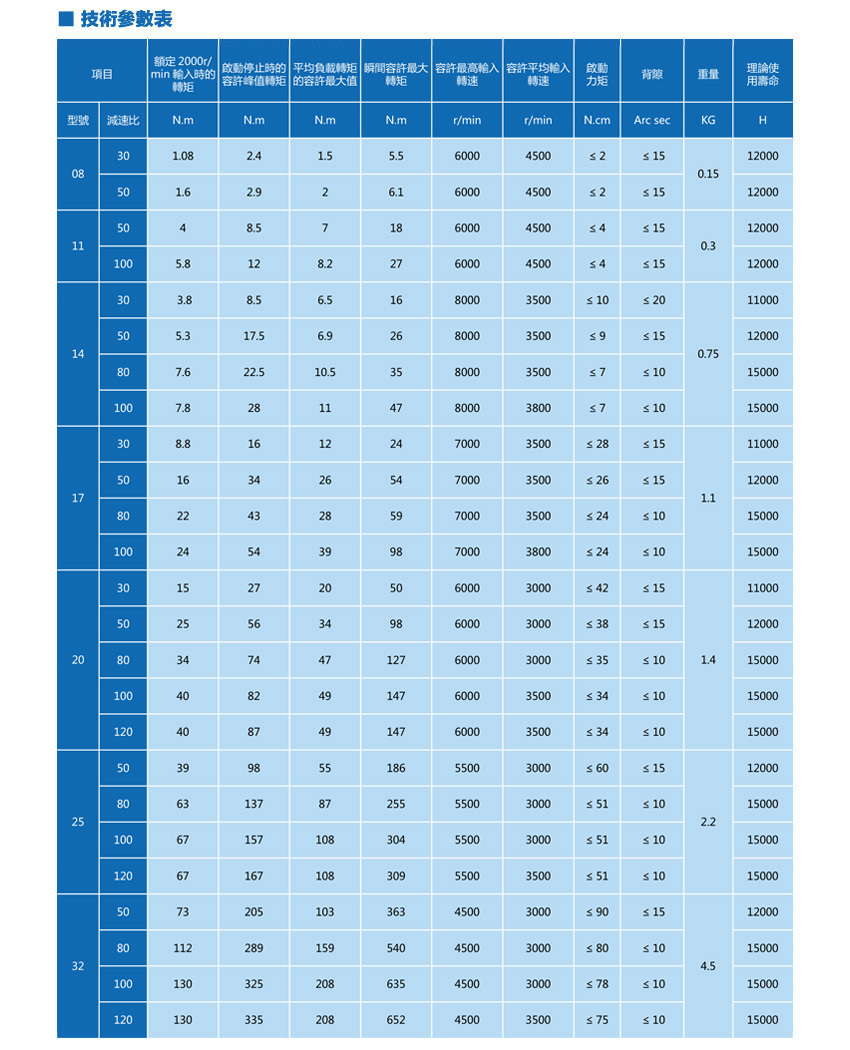
GHS-A corresponding specifications:
GHS08-30-A GHS08-50-A GHS11-50-A GHS11-100-A GHS14-30-A GHS14-50-A GHS14-80-A GHS14-100-A GHS17-30-A GHS17-50-A GHS17-80-A GHS17-100-A GHS20-30-A GHS20-50-A GHS20-80-A GHS20-100-A GHS20-120-A GHS25-50-A GHS25-80-A GHS25-100-A GHS25-120-A GHS32-50-A GHS32-80-A GHS32-100-A GHS32-120-A -
GHS08-A
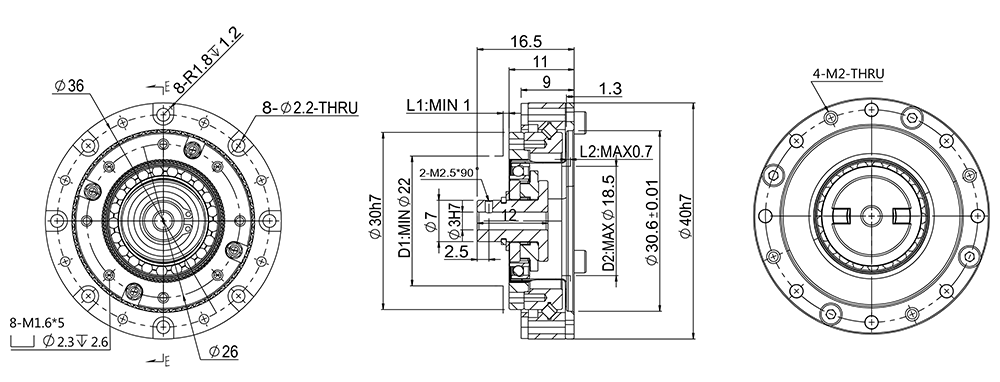
GHS11-A

GHS14-A
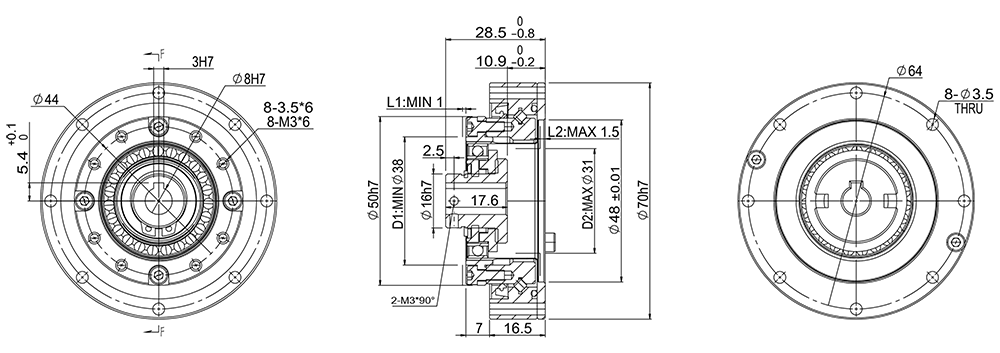
GHS17-A
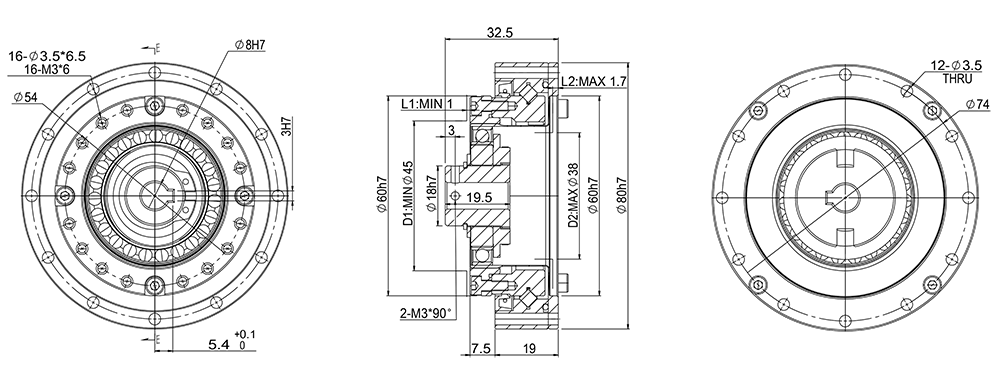
GHS20-A
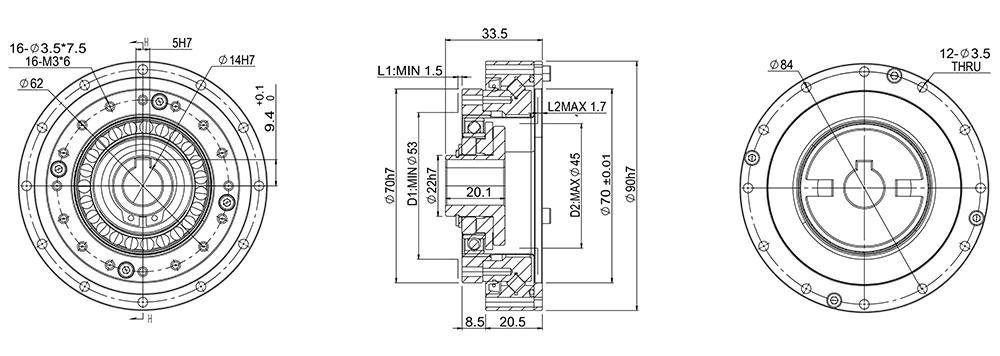
GHS25-A
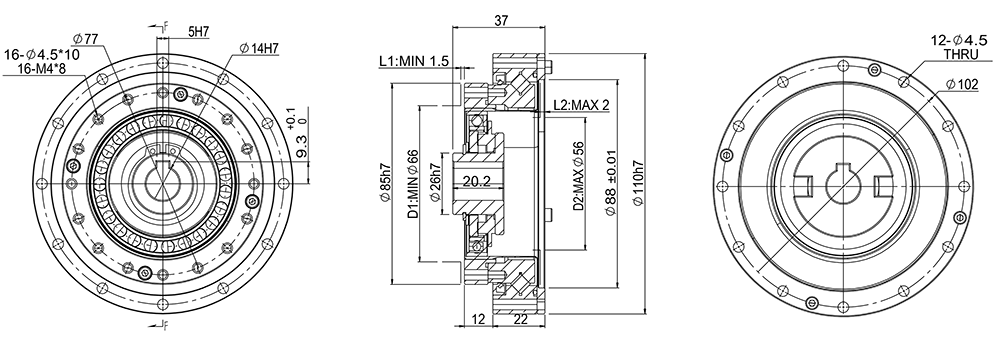
GHS32-A
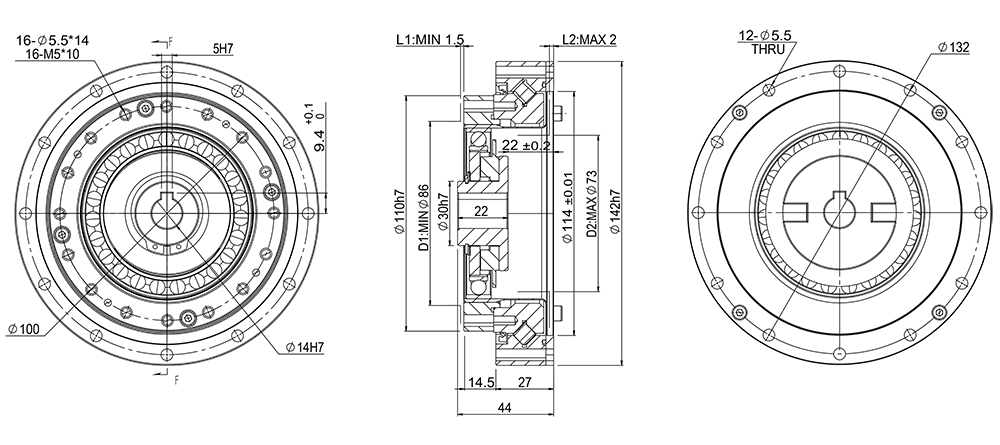
-
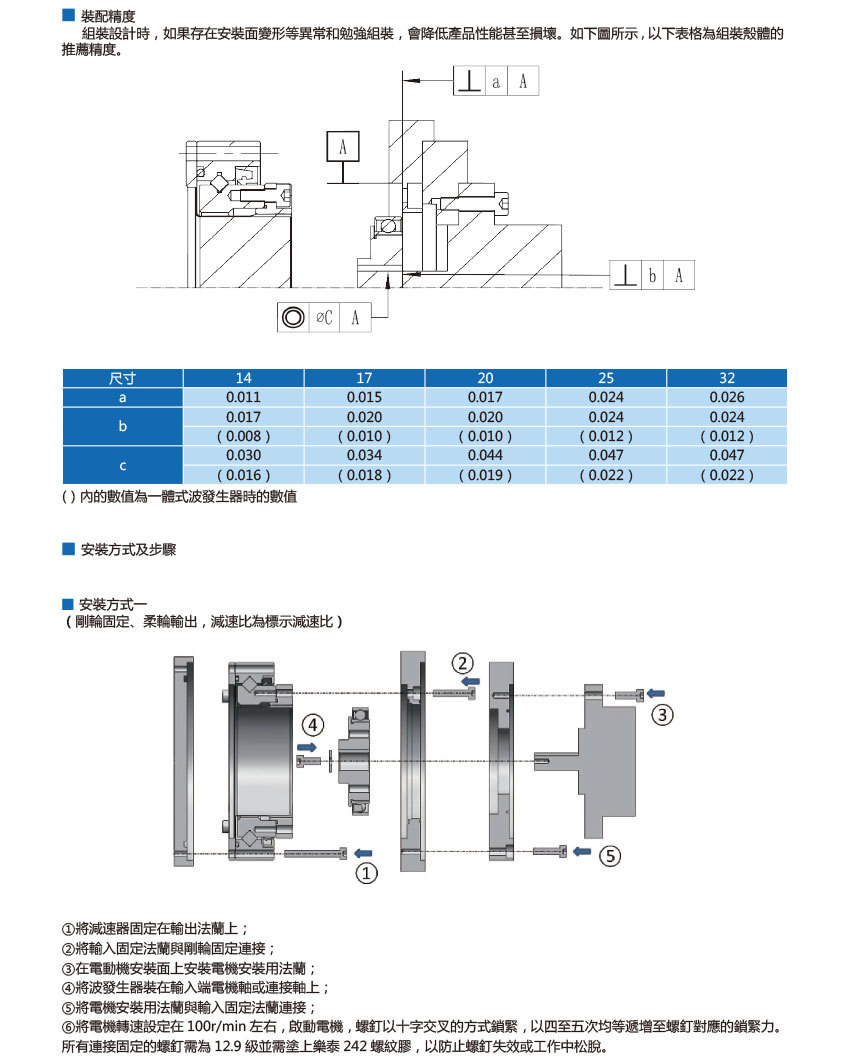
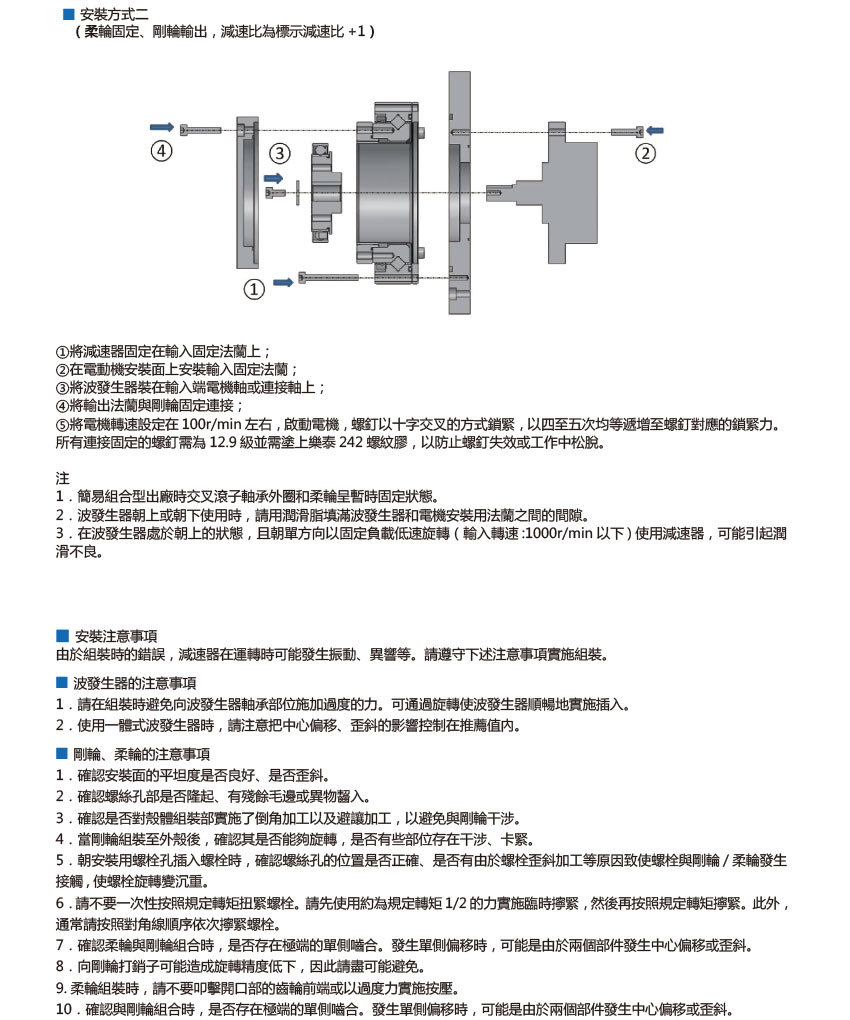

Contact Us
Mobile: +86-13929223395
Tel: +86-769-87782670
E-mail: sales@gigager.com
Add.: Room 1101, Building 28, Zhongji Zhigu, Songshan Lake, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China

Follow Us
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.
Copyright 2025 Guangdong GIGA Precision Technology Co.,Ltd All Rights Reserved粤ICP备12008284号SEOPricacy Notice

